-
N Nitrogen
Nitrogen (N) is essential for plant growth and is part of every living cell. It plays many roles in plants and is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis. Plants take up most of their N as the ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ion. Some direct absorption of urea can occur through the leaves, and small amounts of N are obtained from materials such as water-soluble amino acids.

-
P Phosphorus
One of three primary nutrients, phosphorus (P) is essential for plant growth, and a plant must access it to complete its normal production cycle. Plants absorb P from the soil as primary and secondary orthophosphates (H2PO4- and HPO42-).

-
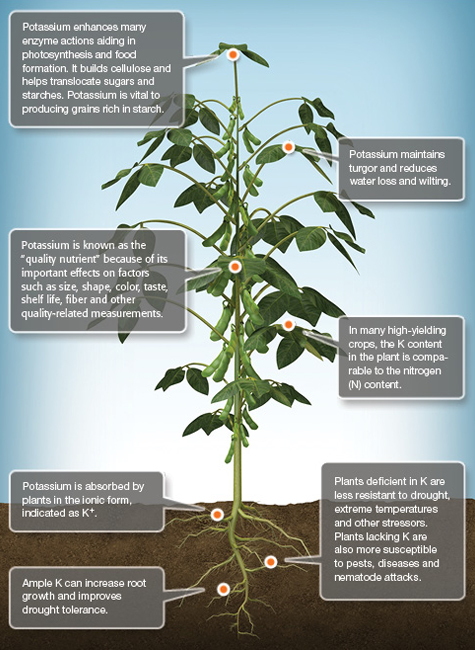
K Potassium
Potassium (K) is one of the essential nutrients and is taken up in significant amounts by crops. Potassium is vital to photosynthesis, protein synthesis and many other functions in plants. It’s classified as a macronutrient, as are nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P). Plants take up K in its ionic form (K+).
-
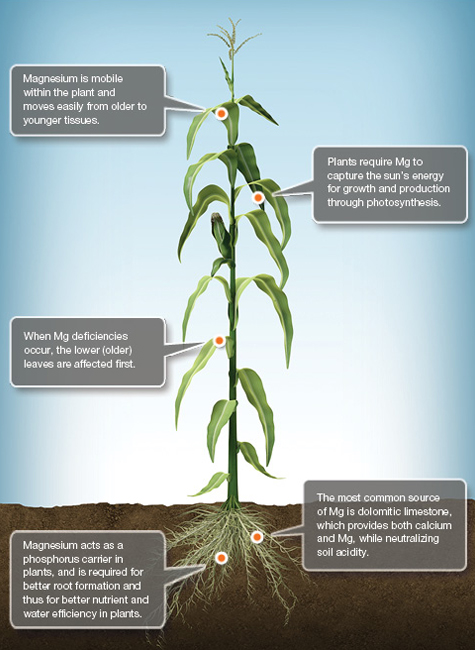
Mg Magnesium
Hidden in the heart of each chlorophyll molecule is an atom of magnesium (Mg), making the nutrient actively involved in photosynthesis. Magnesium also aids in phosphate metabolism, plant respiration and the activation of many enzyme systems.
-
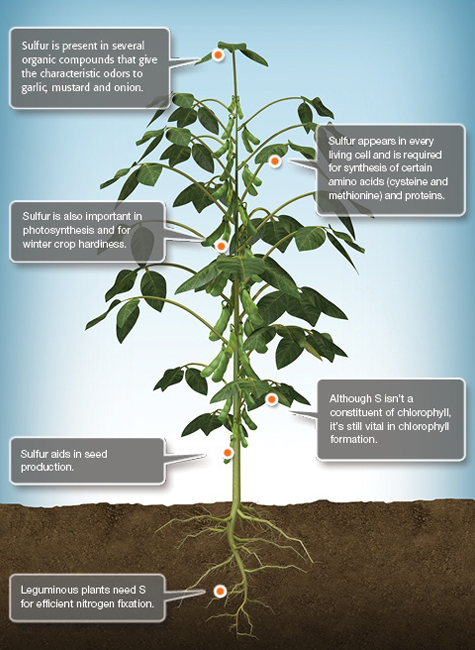
S Sulfur
Sulfur (S) is a part of every living cell and is important to the formation of proteins. Unlike the other secondary nutrients like calcium and magnesium (which plants take up as cations), S is absorbed primarily as the SO42- anion. It can also enter plant leaves from the air as dioxide (SO2) gas.
-
Ca Calcium
Calcium (Ca) is found all around us, and the very existence of plants and animals depends on it. Plants take up Ca as the Ca2+ cation. Once inside the plant, Ca functions in several essential ways.
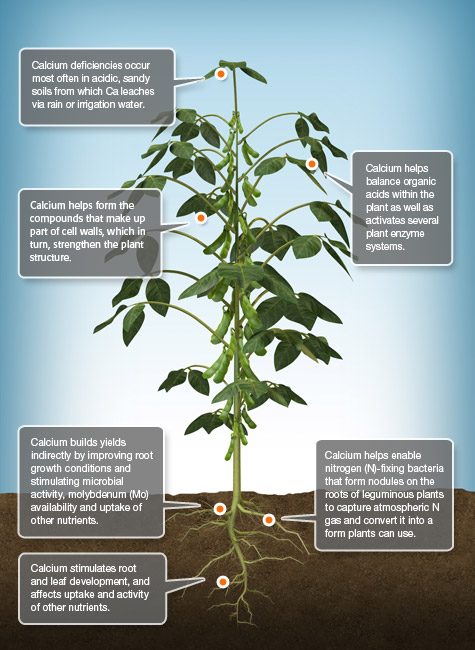
-
B Boron
Boron (B) is a micronutrient that is essential for cell wall formation and rapid growing points within the plant, such as reproductive structures. Interestingly, while higher plants require B, animals, fungi and microorganisms do not need this nutrient.
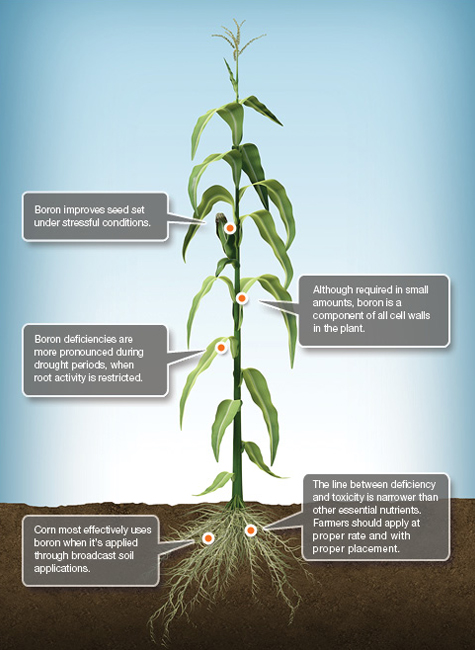
-
Cl Chlorine
Plants take up chlorine (Cl) as the chloride (Cl-) anion. It’s active in energy reactions in the plant. Most Cl- in soils comes from salt trapped in parent materials, marine aerosols and volcanic emissions. Classified as a micronutrient, Cl- is required by all plants in small quantities.
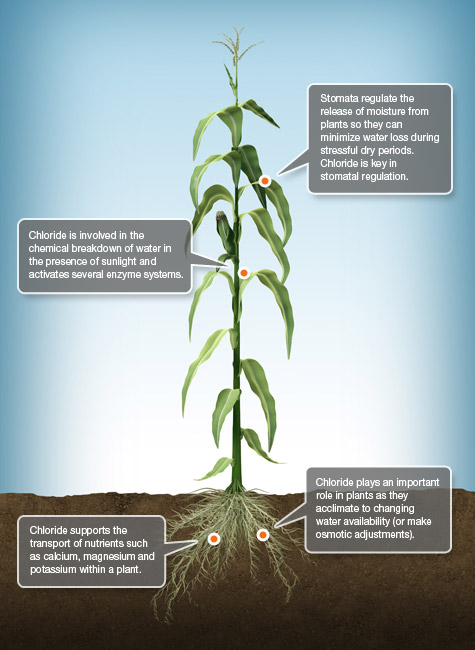
-
Mn Manganese
Manganese (Mn) functions primarily as part of enzyme systems in plants. It activates several important metabolic reactions and plays a direct role in photosynthesis. Manganese accelerates germination and maturity while increasing the availability of phosphorus (P) and calcium (Ca).
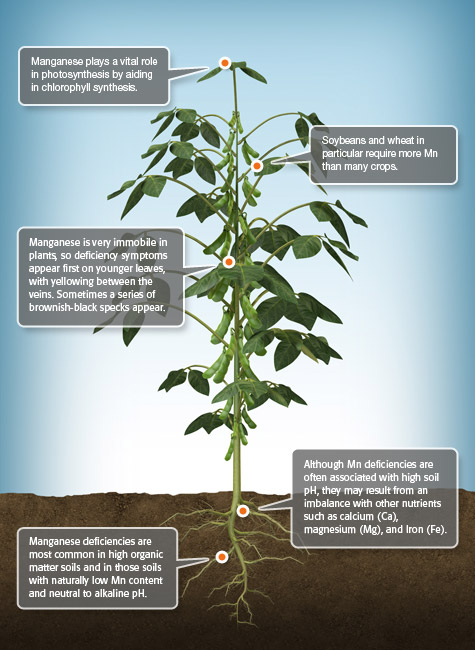
-
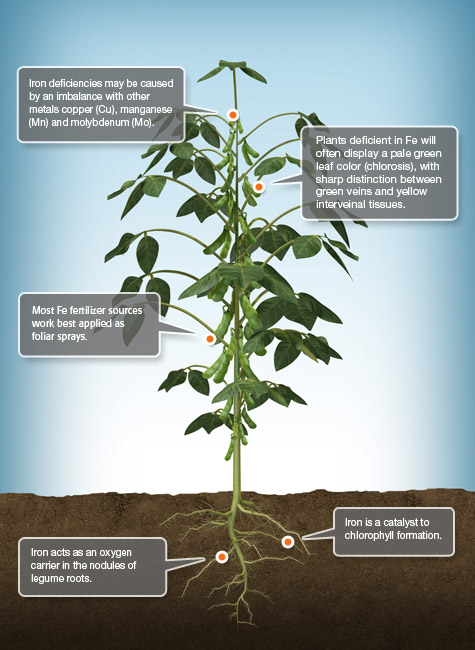
Fe Iron
Iron (Fe) is essential for crop growth and food production. Plants take up Fe as the ferrous (Fe2+) cation. Iron is a component of many enzymes associated with energy transfer, nitrogen reduction and fixation, and lignin formation.
-
Ni Nickel
Nickel (Ni) was added to the list of essential plant nutrients late in the 20th century. Plants absorb Ni as the divalent cation Ni2+. It is required in very small amounts, with the critical level appearing to be about 1.1 parts per million.

-
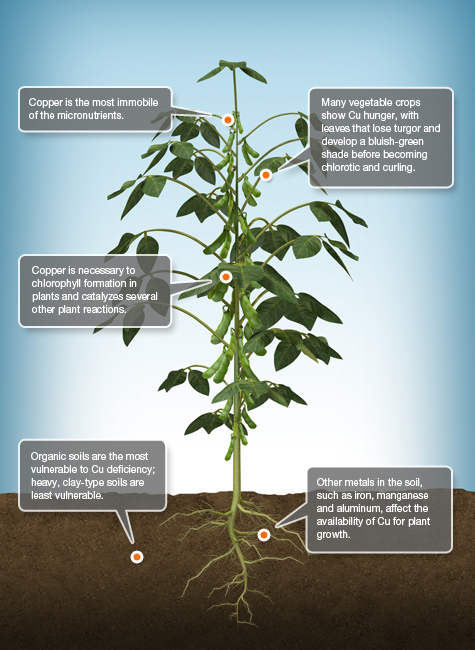
Cu Copper
Copper (Cu) activates enzymes and catalyzes reactions in several plant-growth processes. Vitamin A production is closely linked to the presence of Cu as well, and it helps ensure successful protein synthesis. Classified as a micronutrient, only a small amount of this essential nutrient is needed for plant survival.
-
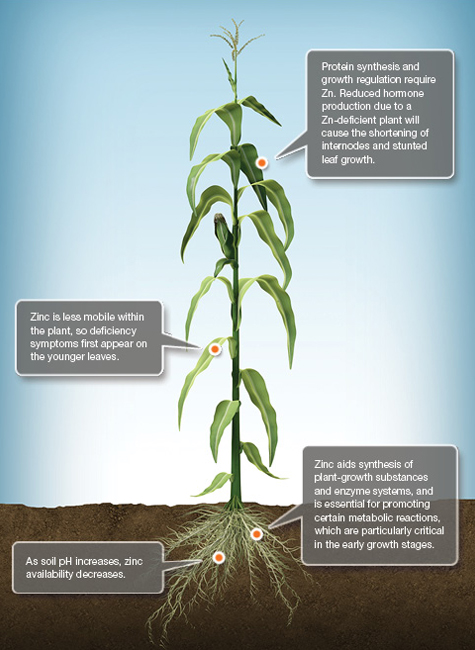
Zn Zinc
Zinc (Zn) is taken up by plants as the divalent Zn2+ cation. It was one of the first micronutrients recognized as essential for plants and the one most commonly limiting yields. Although Zn is required in small amounts, high yields are impossible without it.
-
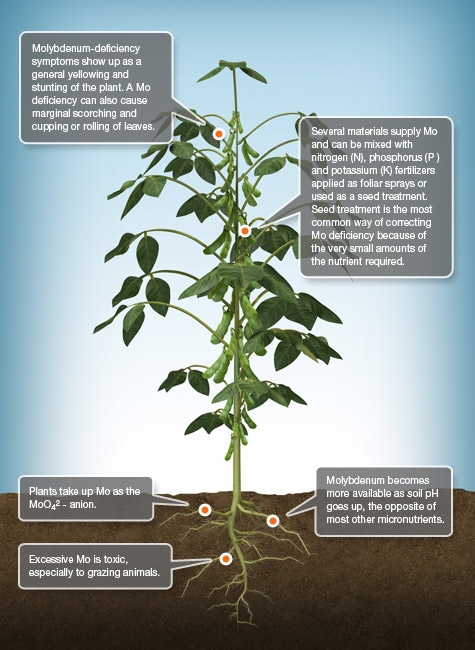
Mo Molybdenum
Molybdenum (Mo) is a trace element found in the soil and is required for the synthesis and activity of the enzyme nitrate reductase. Molybdenum is vital for the process of symbiotic nitrogen (N) fixation by Rhizobia bacteria in legume root modules. Considering Mo’s importance in optimizing plant growth, it’s fortunate that Mo deficiencies are relatively rare in most agricultural cropping areas.
-
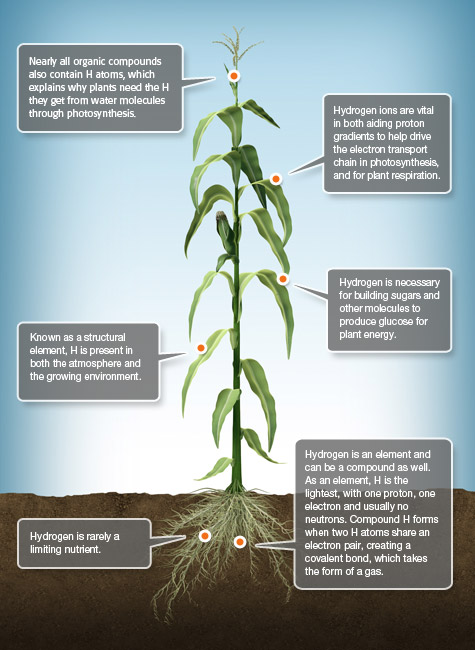
H Hydrogen
Hydrogen (H), derived almost entirely from water, is one of the 17 essential nutrients necessary for plant growth. Hydrogen, along with carbon and oxygen, are the three primary elements plant use in the largest amounts, and they perform as the building blocks for plant growth.
-
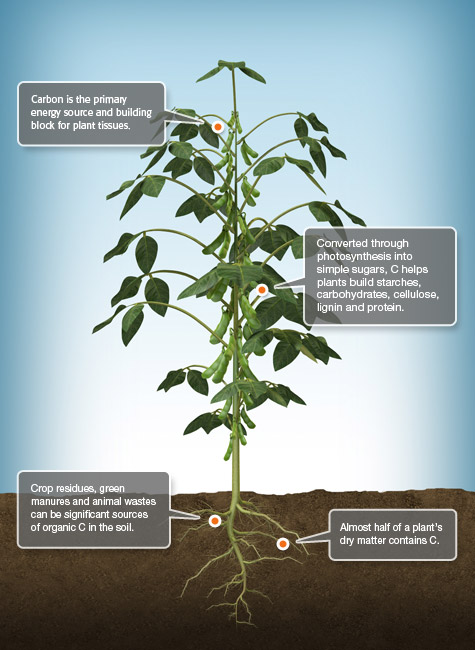
C Carbon
Carbon (C) is responsible for all life on earth. Carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the atmosphere is recycled endlessly as part of the carbon cycle. Plants take CO2 from the air and use the C for energy, helping to build essential biological compounds such as carbohydrates and proteins.
-
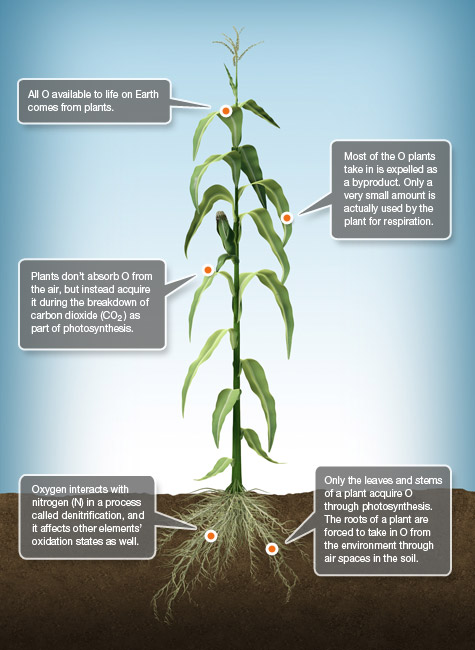
O Oxygen
Oxygen (O) is responsible for cellular respiration in plants. Plants acquire O by breaking down carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis and end up releasing the majority of it as an unnecessary byproduct, saving a small portion for future energy.